ERP System Basics: Must-Have Modules, ERP Architecture, and Best Software Examples
Imagine the worst sales manager’s nightmare: the company’s selling products online they don’t actually have in physical stock. So the staff needs to call the client and apologize for not being able to deliver the order. In situations like these, it’s much easier to lose customers than gain.
But if you have an ERP system with in-built inventory management module, your sales department can sleep well. Besides, ERP software is good for reconciling financials, creating sales forecasts, maintaining order volumes and increasing customer satisfaction. Yes, it can be done using 4-5 different platforms, but managing the data in one place is easier than in several places.
In our article, we’re covering ERP modules and their functions, main architecture types, ERP examples and explaining why to build ERP from scratch is the best choice. So if you want to find out how ERP system works – keep reading.
Types of ERP Modules and Their Roles
Complex systems are usually split into modules depending on the role they perform. ERP software is no different.
I’ve listed several basic ERP modules that companies request most often:
- Human Resources Management (HRM)
- Planning
- Inventory Management
- Building Reports
Let’s review each group in more details.
Human Resources Module
Watching over employees’ performance may be hard even for small-sized companies, not to mention large enterprises. So if you're considering a tech solution for the company, it’s better to stop on custom systems rather than ready-made suites.
Find out more about HR technology strategies and choose one for your company.
By using the system, HR department no longer needs to spend hours on manual performance evaluation or attendance monitoring. Besides, the human resources module also deals with maintaining employees’ contact information, salary details, promotions, and bonuses. So recruiters have all the necessary details at hand and it’s much easier for them to make informed decisions.
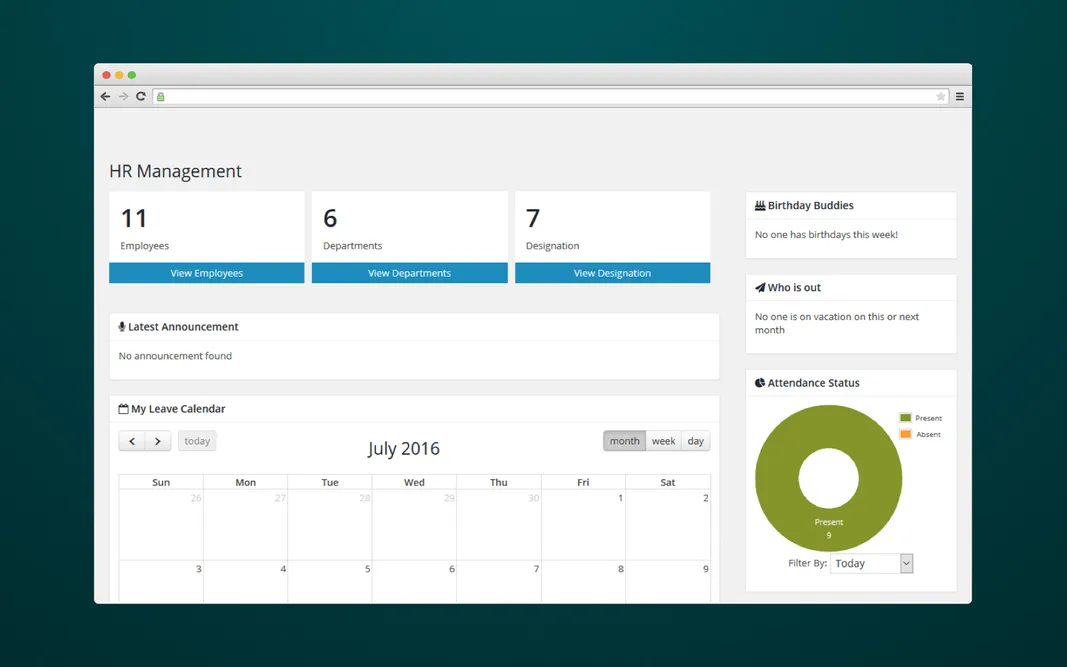
HR management module within an ERP system
Planning
Enterprise planning software also performs data analysis and management. It helps with accessing data and making data-driven decisions besides production planning.
Planning module within an ERP system works great for improving the overall planning process. With the help of the system, managers can easily check information and schedules of various departments or distribute resources more efficiently.
Planning module interface
Inventory Management
As mentioned, the inventory management module is a must-have when working with customers and suppliers. This way, the company’s staff will always be aware of what’s left in their warehouse and what is to be ordered.
Struggle with inventory management? Check our ‘Best Technologies for Warehouse Optimization’ article to be on top of things!
Custom ERP system makes inventory management more flexible and keeps a stable inventory level. So the staff can simply forget about situations when something a client ordered is out of stock.
How inventory management module looks like
Building Reports
Any company, whether big or small, won’t run for long without an established reporting system. And that’s another advantage of ERP systems. Building detailed reports takes a lot of time, still, how else would managers know how successful their business is?
Daily, monthly, quarterly and yearly reports creation and printing is now a matter of a few minutes. And by using filters, the staff will remain sure that their reports contain only relevant details.
How reporting interface looks like
As you can see, custom ERP software helps to automize various processes. There’s no need to buy four different programs which are often complex and have a number of non-required features. In addition, don’t forget about UI/UX design. It’s hard to use poorly designed systems, and employees spend tons of time learning how to work with them.
Types of ERP Architecture
Currently ERP systems are divided into two categories: monolithic and postmodern. Each type has its own characteristics and different levels of flexibility. So it’s time to explain ERP architecture in detail.
Monolithic Systems
These systems have all the needed business management tools in one suite or application. They are developed with a single tech stack and by a single vendor. This way, users always know whom to contact if there’s any performance issue. So despite their implementation cost, traditional systems were able to find their customers, gaining a significant market share.
Our QA Engineerscheck every part of the product, so there will be no bugs or performance issues left.
But nowadays business owners have no interest in monolithic ERP systems that seem complex and are not flexible to business changes. In addition, small companies cannot afford to replace the whole ERP suite with each new process update as the system requires.
Postmodern Suites
Postmodern suites are more simple and user-friendly, compared to their predecessors. They are agile and do not contain lots of redundant tables and other complex solutions that were required for scalability in monolithic systems. And unlike traditional systems, postmodern ERPs are based on a few applications, not a single suite.
They do have core ERP modules, but they can be easily extended with external solutions. For example, basic modules would cover financial and order management, while additional solutions can help with HR or service quality management. Postmodern suites are moving with the times so they are driven by social media, mobile trends and cloud-based solutions.
Comparing monolithic systems with postmodern suites
ERP Software Examples
Now, let’s review the most popular ERP system examples, including their features, focuses, and flexibility.
SAP ERP
SAP SE is the largest European software enterprise based in Germany, and its most popular product is SAP ERP software. The system collects and combines data from various modules and ensures accurate enterprise resource planning. Its main modules include financial and asset accounting, QA management, HR management, product planning and many other.
It’s also possible to customize the ERP suite according to the business needs of a company. ABAP is the primary programming language used to write SAP customizations.
SAP ERP system
Oracle ERP Cloud
Oracle Corporation (USA) is famous for its CRM solutions and flagship Oracle database. But their ERP systems also play an important role in the company’s success. Oracle Enterprise Resource Planning Cloud is used for finance, project management, risk management, procurement, and other everyday business activities. The system has cloud ERP architecture and can be easily customized. In order to create extensions, developers may use standard technologies like JAX-RS/REST, JAX-WS web services, JavaServer Pages, servlets, etc.
The ERP design and architecture are built according to modern trends and technologies. So Oracle ERP is connected with other Oracle enterprise cloud applications and scales to support added users, transactions and sites.
Oracle ERP software interface
Benefits of ERP Software and Why to Build It
In today’s business environments, it’s hard to move on without an ERP system. Among the main benefits of ERP implementation is automatization of manual tasks staff spends hours on and thus improves the overall business performance. So the staff can focus on more important initiatives. At the same time, you can collect real-time data for improving performance management and making data-driven decisions.
ERP software comes handy in lots of areas due to its in-built modules and flexibility. Here are a few advantages of ERP software:
1. Reduce operating cost
The company starts gaining profit as soon as the ERP system is implemented. Prepare to face the reduction of marketing expenses, inventory maintenance, production cost and so on.
Also, if you’re aimed at combining all business processes within a unified system, ERP is the right choice. By using the software, it’s easy to improve cross-department cooperation and increase staff’s efficiency.
2. Instant data access
With ERP systems, employees soon forget about hours spent on collecting necessary details. Instead, they can be accessed in just a few minutes. Works great for busy executives and department managers that need to access data quickly.
3. Defined planning process
It’s easy to understand the business objectives, targets and aims when you have a full list of business needs, outcomes, and assets all in one place.
Sure, ERP systems also have some disadvantages. The most common issue is the price. It’s almost impossible for small companies to develop an ERP suite for their own needs, only middle and large-sized corporations can afford it.
Contact us to get a full estimation of your project for free.
Still, ERP systems are developed specifically for optimizing business processes within your company. So amortizing the development cost won’t take much time. By the way, you can start with building a suite of one-two standard ERP modules, adding more when the need arises.
Let’s Build It Together
At Cleveroad, we provide enterprise-level software development services, including the development of complex ERP business solutions. So if you need to consult with an experienced team or looking for developers to bring your ERP system to life, don’t hesitate to drop us a line. Our managers will gladly answer all of your questions and estimate the price of your project for FREE.
Here are the advantages of ERP systems:
- Reduced operating cost
- Instant data access
- Defined planning process
Currently ERP systems are divided into two categories: monolithic and postmodern.
- Monolithic Systems. These systems have all the needed business management tools in one suite or application. They are developed with a single tech stack and by a single vendor.
- Postmodern Suites. Postmodern suites are more simple and user-friendly, compared to their predecessors. They are agile and do not contain lots of redundant tables and other complex solutions that were required for scalability in monolithic systems. And unlike traditional systems, postmodern ERPs are based on a few applications, not a single suite.
SAP SE is the largest European software enterprise based in Germany, and its most popular product is SAP ERP software. The system collects and combines data from various modules and ensures accurate enterprise resource planning. Its main modules include financial and asset accounting, QA management, HR management, product planning and many other.
- Human Resources Module
- Planning
- Inventory Management
- Building Reports
Enterprise resource planning (ERP) is the integrated management of main business processes, often in real time and mediated by software and technology.
ERP systems reduce marketing expenses, inventory maintenance, production cost, and so on. Besides, they grant instant data access and make a lot of process time-efficient.
Comments