Agile Software Development Methodology: Definition, Types, Workflows
Updated 12 Mar 2023
13 Min
2542 Views
Even a small IT project may require a lot of specialists, tools, reports, and discussions. All that is needed to be managed. However, even with a well-managed development process, it can be challenging to predict difficulties that’ll emerge.
Companies follow agile software development methodology to accelerate software delivery yet be flexible to changes. According to GoodFirms, 61.5% of companies follow Agile methodology because it lets them change priorities fast.
In this article, we’re talking about Agile software development methodologies and practices. You’ll also learn what phases the Agile life cycle consists of when it comes to software development.
What Is Agile Software Development?
Agile is a mix of values and principles that are described in the Agile Manifesto. The primary goals of Agile are to accept the change, constantly make improvements, and deliver a working product as quickly as possible.
There are many software development methodologies, and each of them has its own specific features and areas of use. Here is an example of the most popular Agile methodologies:
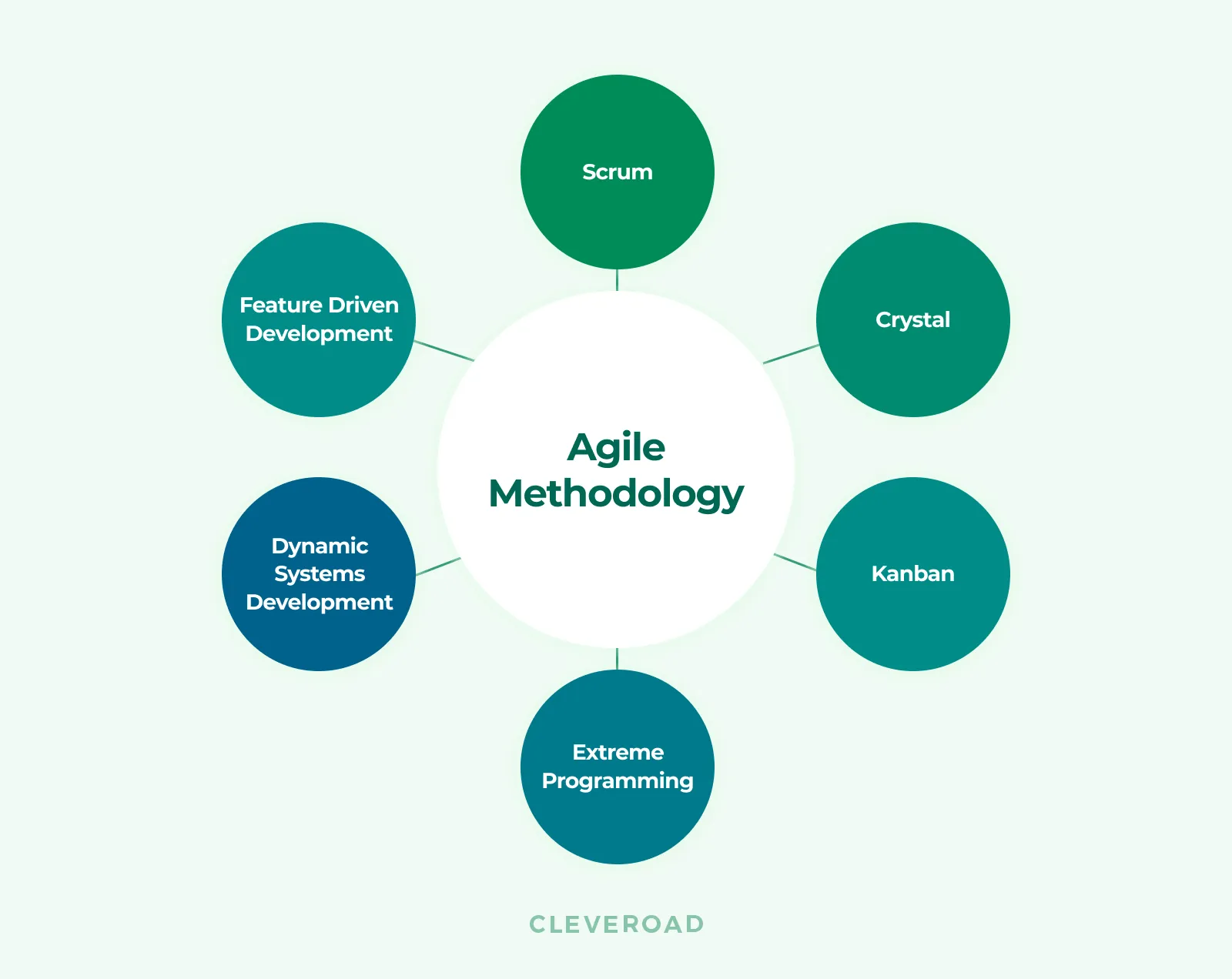
Types of Agile methodology
Even though their principles are aimed at meeting customer requirements and delivering a high-quality product, each methodology uses a slightly different approach to organize software development. For example, Scrum uses sprints (two-week time periods), while Kanban is basically a bunch of tasks on a board.
All Agile frameworks are based on the underlying principles:
- Focus on customer needs, not instruments
- Everything can be changed at any stage of development
- Clients and developers have to cooperate throughout the development
- Set the appropriate environment and provide all essential tools to develop the project
Those rules have made Agile popular, encouraging the emergence of Scrum, Kanban, Lean, and other frameworks inspired by Agile principles. They’re now one of the most in-demand software development methodologies, which we’ll talk about a bit later.
Talking about Agile software development, one of the most common questions is what are the roles and responsibilities in an Agile team? Depending on the framework, project size, and its particularities, roles in a team can change. Each employee can hold one or more roles and switch between them anytime.
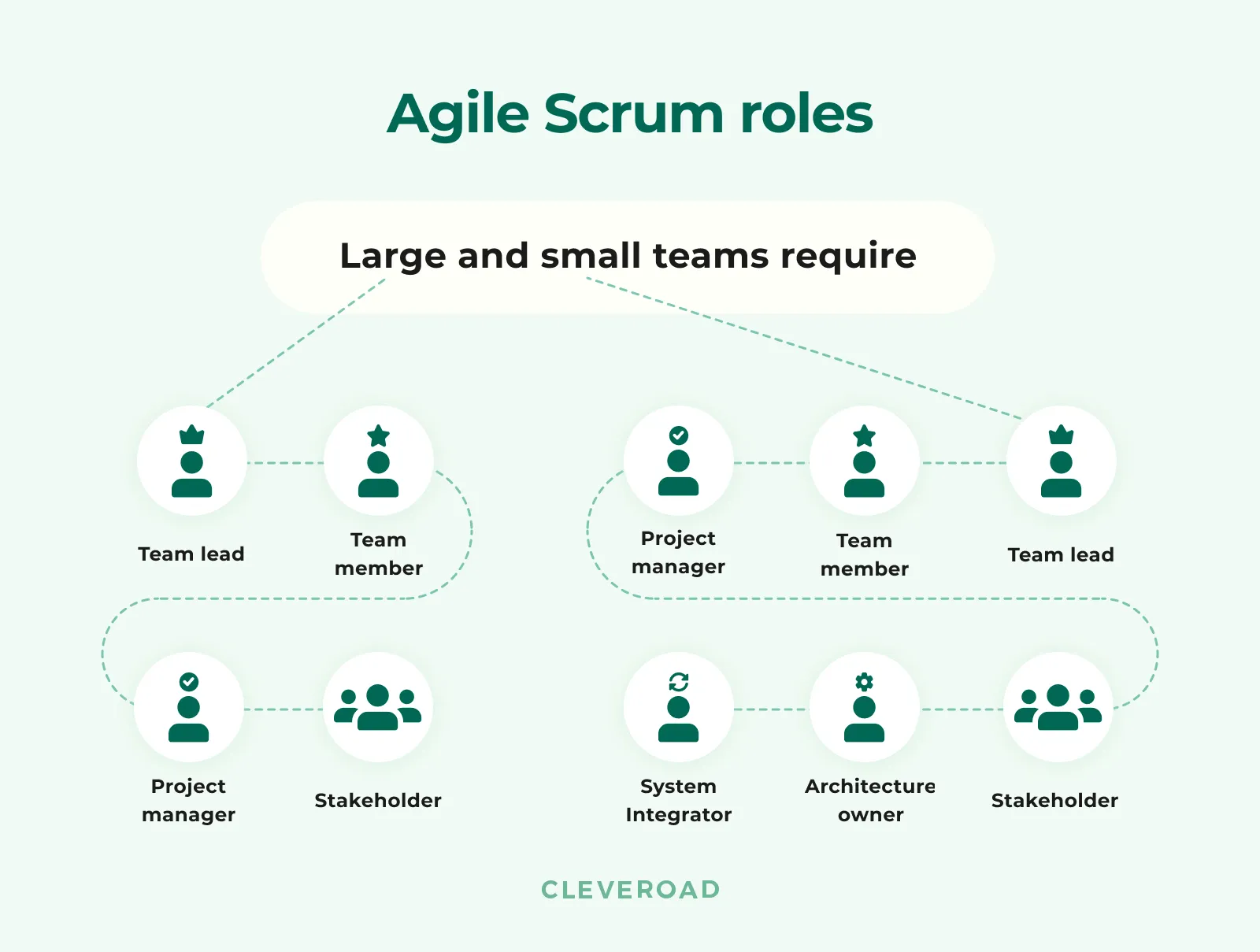
Scrum small and large team roles
We’ll briefly outline the main roles we have in our development teams at Cleveroad, but generally, they can differ from company to company:
Team lead
In Agile teams, the leader helps the rest of the team follow the time-tested product development process. The team lead manages the team, provides necessary environment and tools and removes all obstacles on the way.
Team member
In short, it's a group of people (business analysts, software developers, QA engineers, UI/UX designers, DevOps) working on the project together as a team. They’re responsible for building and releasing the product.
Project manager (PM)
This role transfers the customers’ vision to the team and manages Product Backlog. The project manager is responsible for project implementation and delivering the product according to initial requirements. Unlike the team lead, project managers don’t manage the team, they negotiate with them to map progress or identify problem areas.
Stakeholder
Stakeholders are everyone involved in the product. It can be people involved in the development process, customers, sponsors, future users, and others.
This is a small software development team structure in the Agile software development process. In the case you have a big project, you may need several additional roles like:
Architecture owner
This role is crucial when you have a large development project. Architecture owners are responsible for developing the project’s architecture.
Integrator
Integrator is responsible for system integrations after each sprint. For example, if two programmers implement new features on separate components A and B, and each thinks their work is done, then checking that changes to A and B are the Integrator’s duty.
Benefits of Agile
Clients' requirements may change pretty often, so product owners should keep the team updated whenever the product needs additional changes. Agile methodology is a perfect option to deliver a superior quality product in a short time. Let’s consider what makes Agile is so beneficial and why many companies use it.
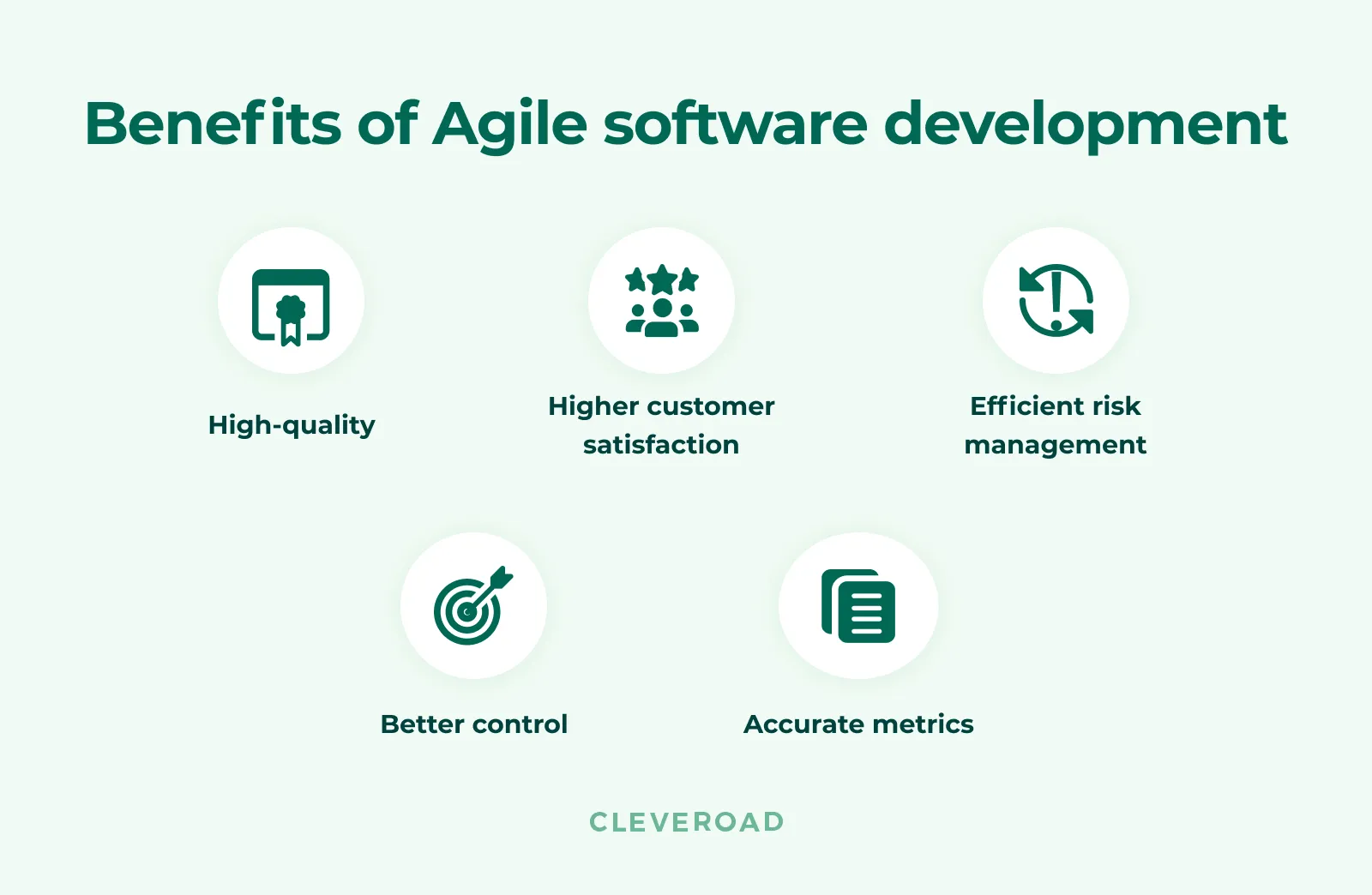
Main advantages of Agile methodology in software development
High-Quality Product
Breaking down a complex product into smaller parts (sprints, Kanban tasks), the development team can focus on quality and collaboration. Moreover, regular testing and reviews after each iteration let your team find and fix bugs and define the mismatches between customers’ expectations and the product in the early stages.
Higher Customer Satisfaction
Customers take part in the decision-making process, which increases their involvement. While customers are only a part of a planning stage in the traditional model, they take an active part in the development process in Agile, which affects the product's flexibility and adaptability. Keeping your customers in the loop, you’ll be able to make changes based on their regular feedback and deliver a product that truly matches their requirements.
Efficient Risk Management
Users won’t use a product that works slow or has many bugs. Since Agile focuses on the delivery by iterations, there’s always a chance to make improvements at the end of each iteration. Besides, the Agile software development team can fix the bugs as quickly as possible, and all potential risks will be managed on time.
Read our article on how to deal with risks during your project’s development.
Better Control
Since Agile projects are transparent, focus on key features, and based on customers’ feedback, project managers have more control over the development process. Quality is ensured throughout the development lifecycle, and all stakeholders are involved in the project.
Accurate Metrics
Agile software development methodology uses more relevant and precise metrics to estimate the project performance compared to traditional models. Agile focuses on getting good results and optimizing performance due to user requirements, while the metrics in Waterfall methodology emphasize on time estimation.
Agile adopts critical metrics like lead time, cycle time (helps to measure the team's productivity), identify weak spots, and make the right decisions to strengthen them.
Agile Software Development Methods
Agile methodologies are frameworks and practices that assist in software development service using different iterative or incremental development techniques. The difference between Agile methodology and its frameworks is that the latter are more formal and have strict rules.
Below, you’ll find the most commonly used Agile methodologies.
Scrum
According to the Annual State of Agile Report, 58% of companies use Scrum to manage their working process.
Scrum works with sprints (fixed periods) during which the developers implement a certain part of the product. Sprint starts with the planning stage and ends with the delivery of a pre-established product.
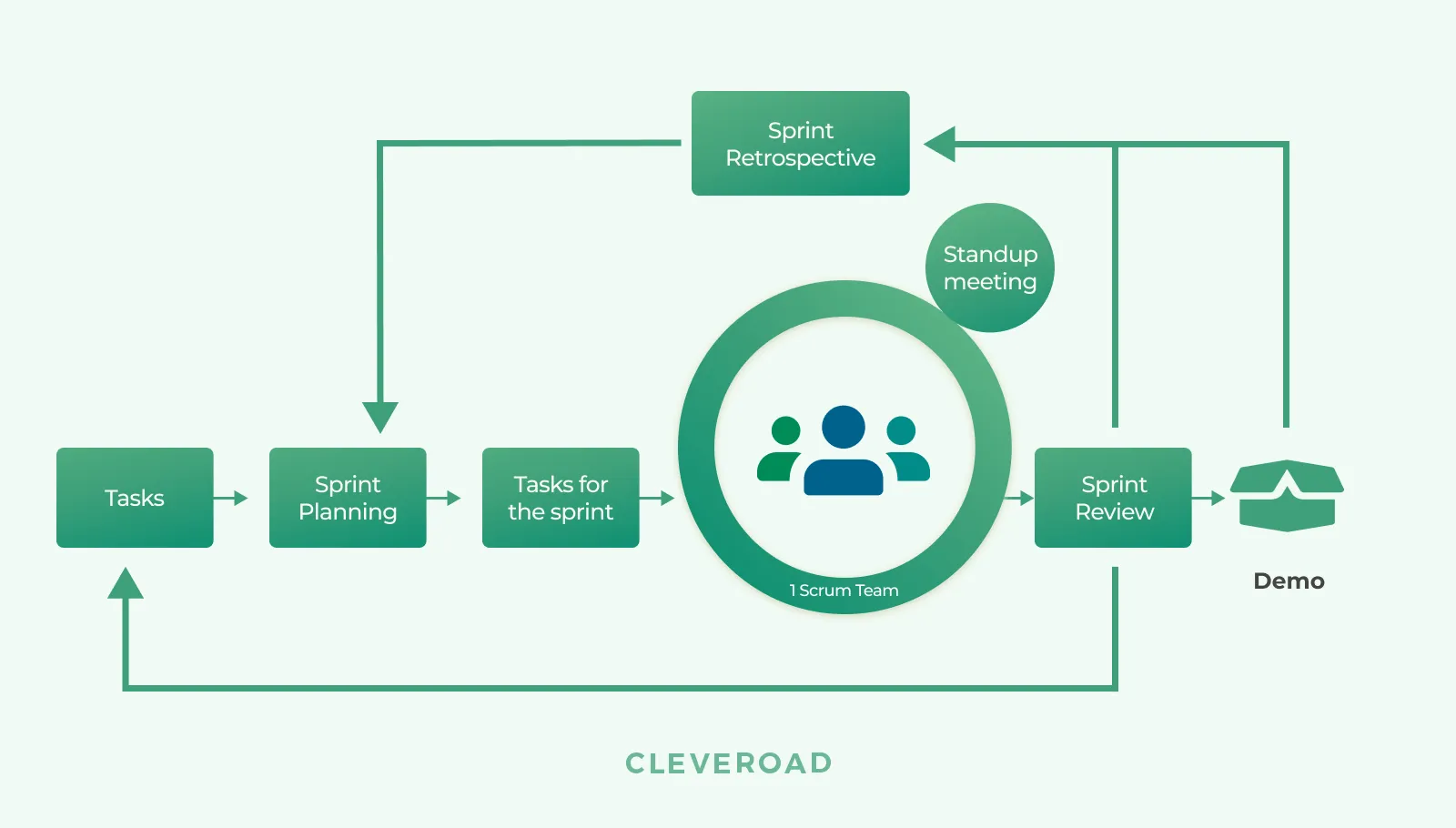
Scrum methodology for software development process
Traditional Scrum elements are:
- Sprint planning meeting. Before the work starts, the team meets with the client to discuss the features for the sprint (usually lasts two weeks).
- Daily meeting with Scrum Master. Each day during the sprints, team members discuss what they did yesterday, what they’re planning to do today, and what blockers they’ve encountered.
- Review. The project manager demonstrates new functionality to the clients and gathers their feedback.
- Retrospectives. The team holds a meeting to review what’s gone wrong during that stage and where they’ve made good progress to resolve such situations faster in the future.
Scrum is based on high client involvement and careful planning. It’s a great choice for MVP development that requires consistent improvements.
Kanban
Kanban focuses on seamless task competition without splitting them into sprints. Let’s see how it works:
- Traditionally, the workflow is divided into three stages — To Do, In Progress, Done
- Every task is marked with cards
- After developers complete the task, they move the card to the next stage
Unlike Scrum, Kanban doesn’t have a sprint backlog. The Kanban board has a set of tasks to do. After the team finishes a part of the functionality, the Project Manager writes a new card with a task and puts it on the board. Moving cards along the board helps stakeholders understand what time it takes to build a feature. Thus, it’s possible to predict a project duration.
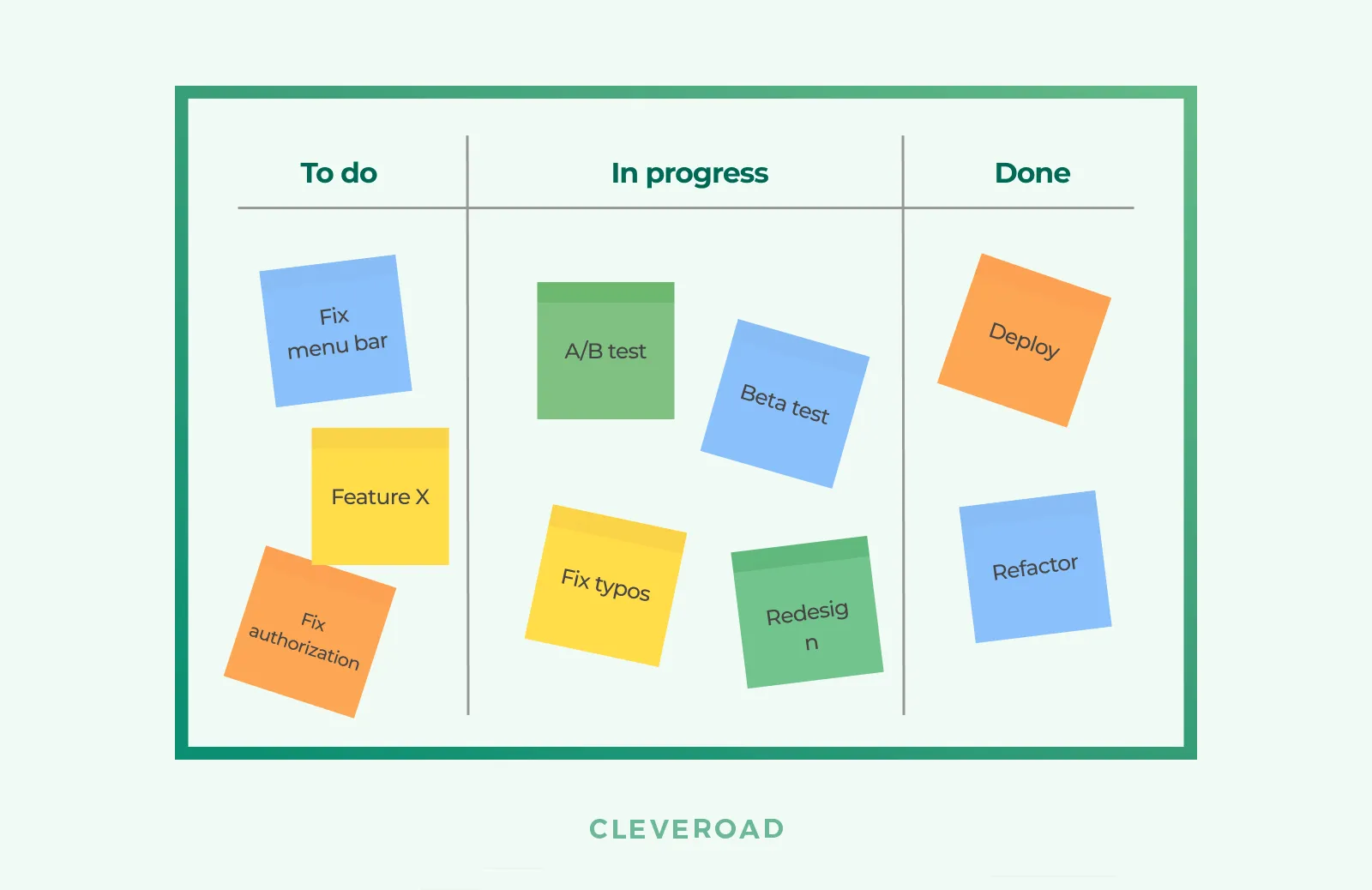
Kanban board
Lean Development
The main purpose of Lean methodology is to deliver tangible value to customers with minimum expenses and defects. Put simply, it means creating a product that requires fewer efforts, less money, and time. The lean methodology follows a clear process and has strict acceptance criteria.
The main purpose of Lean development is to eliminate waste
Dynamic Systems Development
DSD clarifies the role and responsibilities for everybody involved, along with proven techniques to help the project team satisfy business needs. It’s based on four principles:
- Put quality over functionality
- Deliver on time
- The final product is more likely to be completed exactly as defined, even if better solutions are available
- Strict expense control
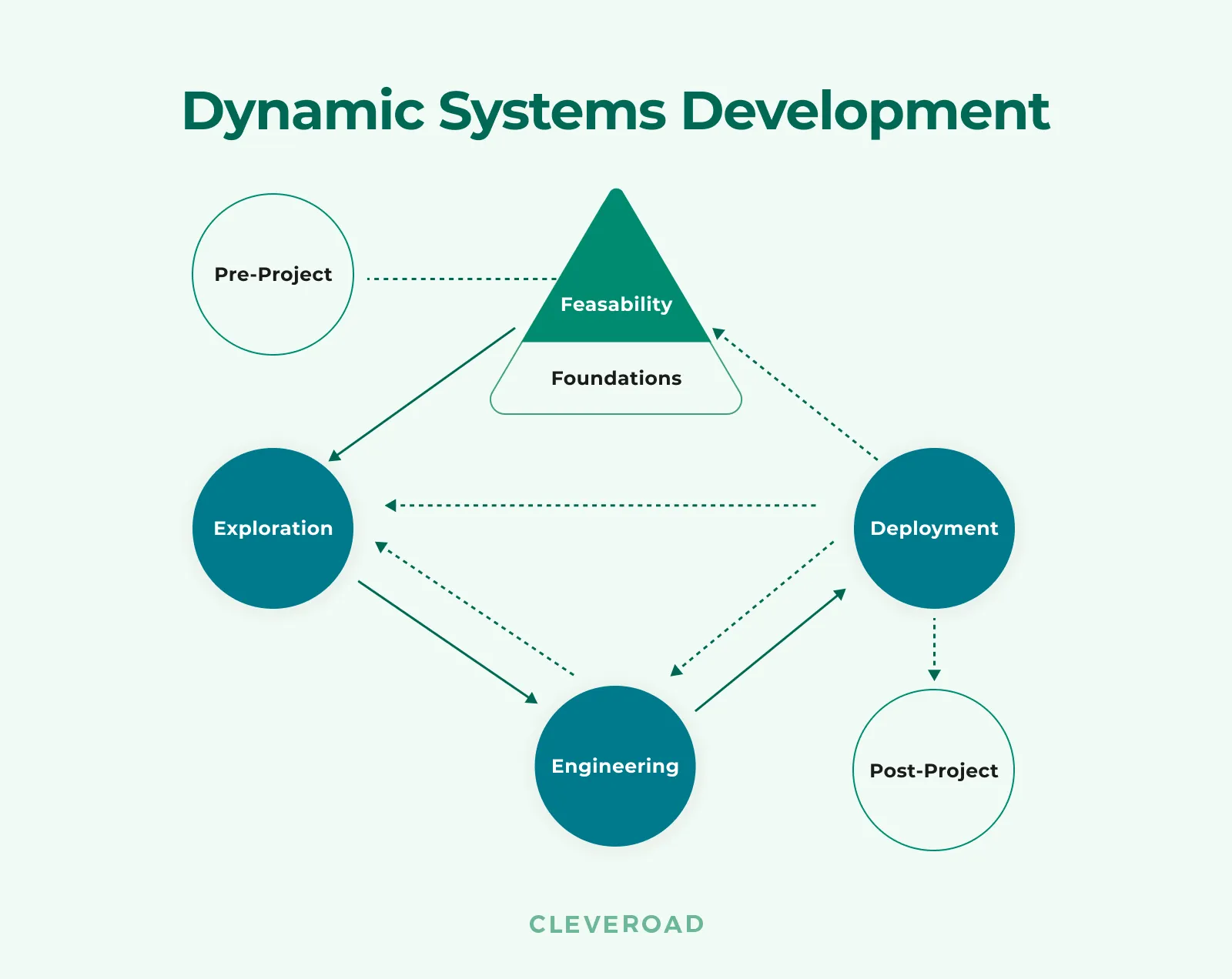
Dynamic systems development process
It’s a good choice if you prefer predictability and consistency over flexibility. However, due to a lack of creativity, it may not be a good strategy for startups.
Extreme Programming
This methodology got its name from taking traditional software engineering practices to extreme levels. It’s based on a specific planning approach, pair programming, sustained testing, continuous integration, and small releases.
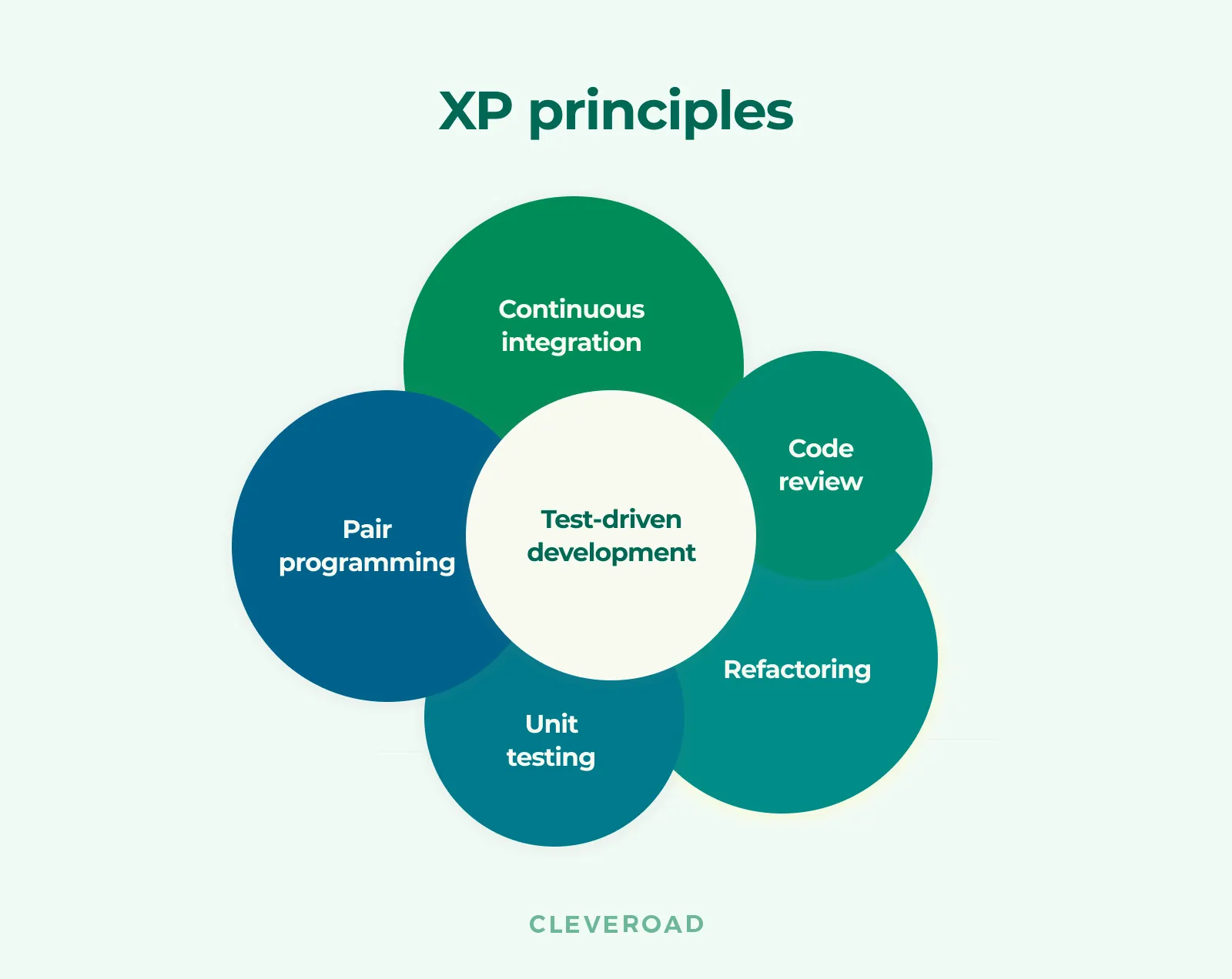
Extreme programming basic principles
Like any Agile software development model, XP starts with planning. The team considers the requirements and sets up the time frames for each task. But instead of writing code first, developers proceed with acceptance tests. These tests define what the code should do according to the requirements.
After testing, two developers work on a piece of code simultaneously and run it through the acceptance tests. Developers integrate the system every time the task is completed.
Read our article reviewing different software development methodologies, their pros, and cons for different business goals.
Feature-Driven Development
Feature-driven development is a feature-centric model based on building an overall product.
It means that you’re developing features bit by bit, getting feedback, and putting them into the products over time to improve them. Its major purpose is to deliver working software regularly in the short term. FDD calculates the product’s readiness based on tasks completed.
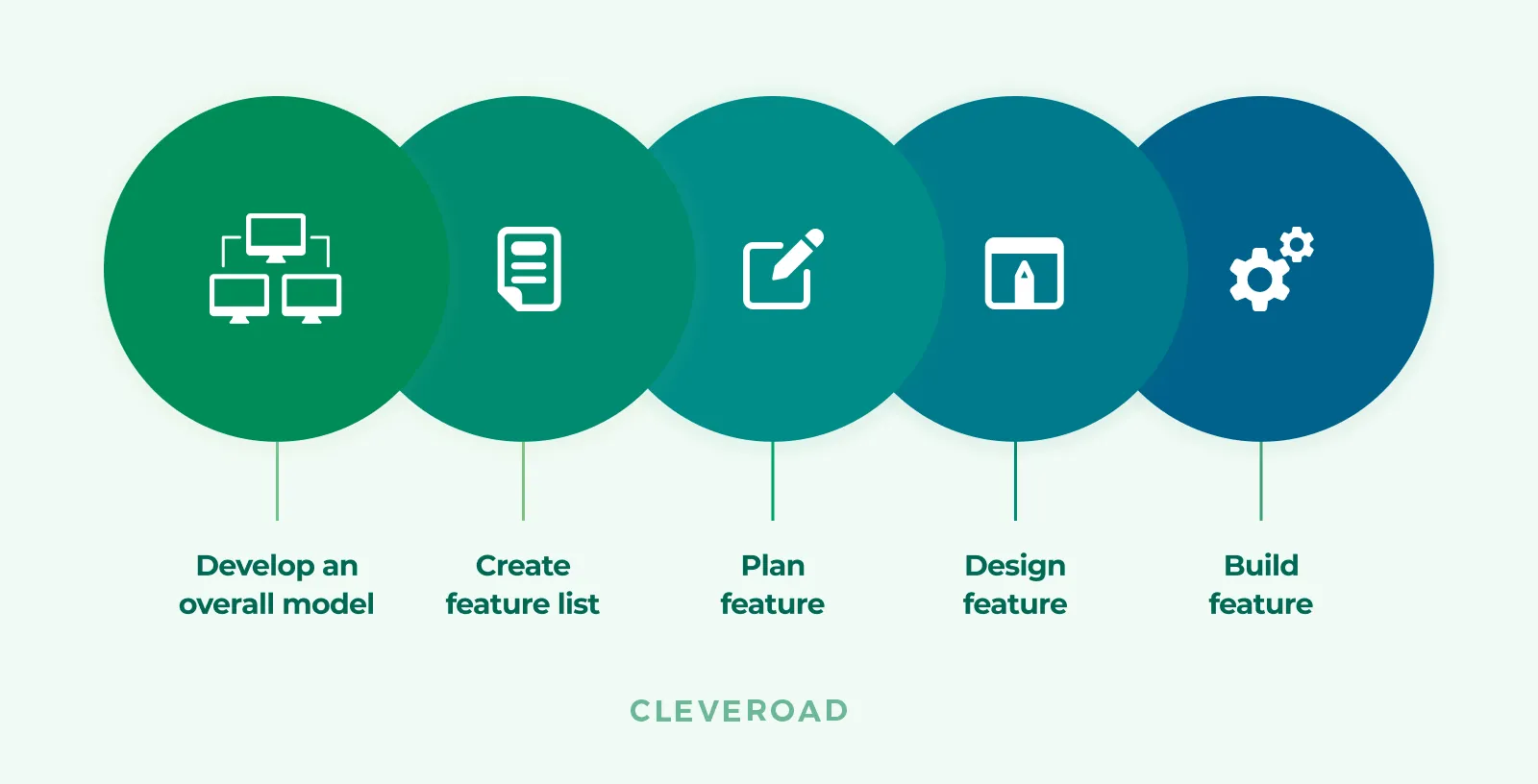
Main steps of feature-driven development
Crystal
The Crystal is probably the simplest and most universal Agile software development method. It focuses primarily on the interaction between team members rather than tools and processes. The future strategy and team size get decided as per the project’s criticality and business priorities.
Crystal focuses on:
- Early product delivery
- High client involvement
- Versatility
- Reducing of distractions
It depends on your project what framework to use. There’s no right or wrong strategy. If you have a complex long-term project, then it’s better to follow Scrum. Lean Development is a good choice for startups seeking to build an MVP. Kanban is often used for small projects.
Agile Software Development Process
The Agile process in software engineering is based on an iterative process. After each iteration, the team moves to the next stage until all the requirements are met.
During those iterations, customers and stakeholders are involved in the project to give feedback and ensure that the product reflects their vision.
Let’s look at the key Agile software development life cycle phases.
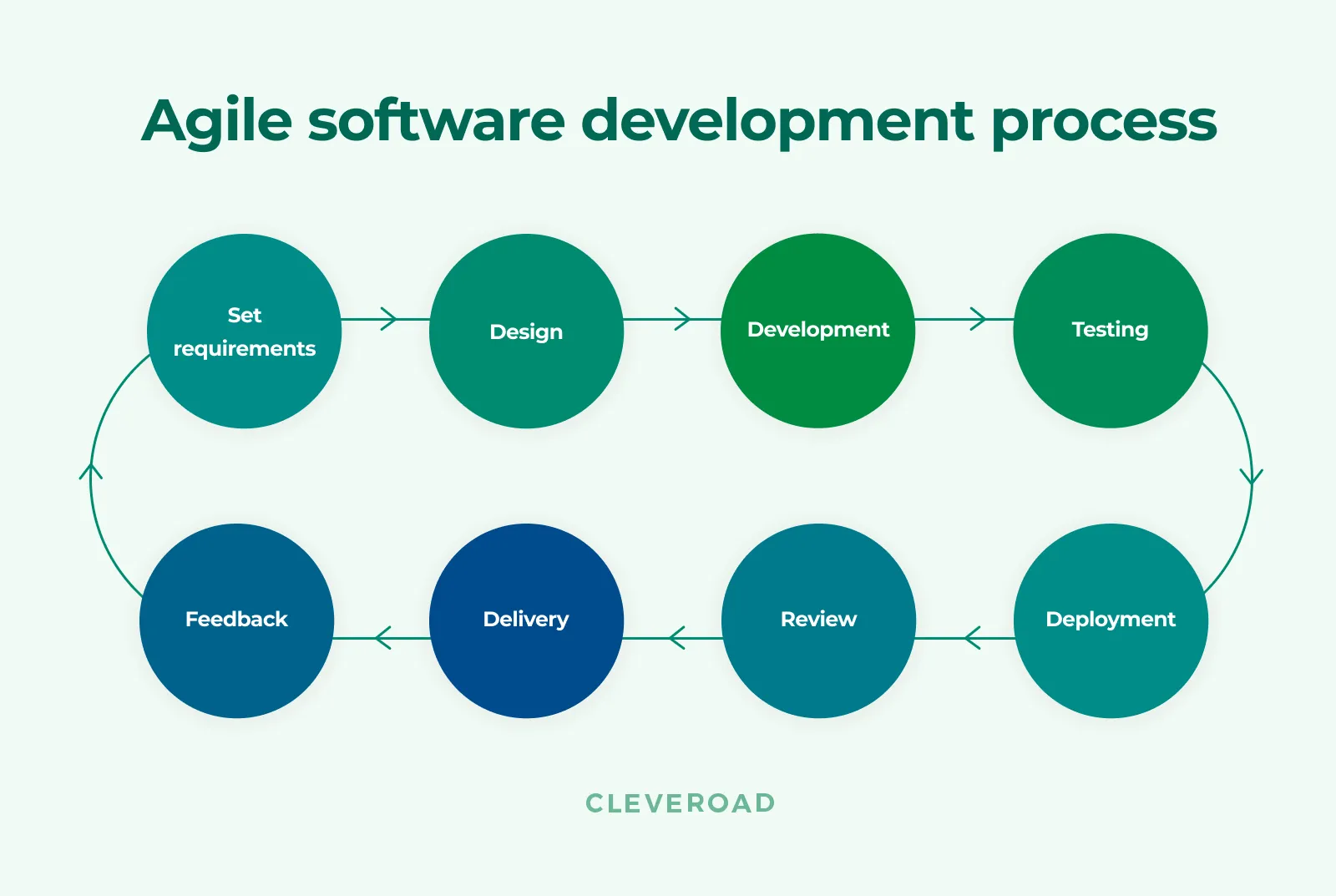
Agile software development life cycle
Phase 1: Requirements
Before starting anything, the customer needs to prepare a list of basic requirements. For example, the product’s impact (increase conversion by 10%, reduce operational expenses by 15%), what features you’d like to include, and so on.
The main goal is to focus on the core features that customers will use, putting aside those that’ll be used rarely. Software engineers can return to them later after the app is deployed and initial features work as expected.
Phase 2: Design
There are two approaches for software design: interface and architectural.
Software Design
During the first script, the Project Manager gathers an agile software development team and introduces the main requirements of the project. After the team considers how to handle these requirements and picks up the tools (programming languages, frameworks) to deliver the first-rate product.
UI/UX Design
The designers create a UI mockup to present a prototype of an app. User interface and user experience are vital elements of any application. It’s better to review potential competitors and analyze their strong and weak points.
Further, the Product Manager accepts the initial design or asks developers to customize it to the new features.
Phase 3: Development
The development stage is about designing and developing the software in accordance with the approved requirements. It’s the longest development phase as it’s the heart of the whole project.
Phase 4: Testing
This stage of software application development services includes QA testing with the further reporting of results before delivery. The QA team conducts multiple tests to ensure that the software is bug-free and consistent with changes that the developers implemented earlier. During the further scripts of this SDLC stage, the testing becomes more complicated and involves not only functionality but systems integration testing, user acceptance testing, and so on.
Do you want to learn more about the software development life cycle? Check our full guide dedicated to Cleveroad’s software development process.
Phase 5: Implementation and Deployment
Once the testing phase is done, the product is deployed on the servers and given to the customers for beta testing or actual use. The support team gathers initial feedback, fixes bugs (if any show up), and introduces new features. After that, the final version is prepared.
Phase 6: Review
The Project Manager meets the Agile development team once again to review if the product is market-ready. The team introduces the solutions towards fixing the problems that came upon the previous iterations, and the Project Manager considers their ideas.
Phase 7: Delivery
Once all previous development phases have been passed, it’s time to deliver ready-made solutions to the customers and stakeholders.
Phase 8: Feedback
Collect the users' feedback and consider this information to improve the product in the next iterations.
Wrapping Up
Agile software development methodology has many benefits both for the development team and for as it requires regular client involvement and makes it possible to change the work scope any time without affecting the entire development process. The only thing you need is an experienced development team that’ll transform your idea into a fully-fledged solution.
At Cleveroad, we use Agile methodologies and work with the Scrum framework on our projects. Scrum helps our clients remain flexible and easily make changes to their projects.
That’s how we’ve helped a startup called Ayoo launch — and keep helping to improve it.
Want to build your product?
Tell us about your project, and we'll help you find the best approach to its delivery.
The Agile software development is a mix of practices when the software development process breaks down into iterations and requires high involvement from the client’s side.
Agile software development processes consist of certain iterations. Each iteration results move to the next stage of software development until the final product is done.
Agile software development model applies to any situation, whether you have a startup, need to fix some bugs, or have a long-term, complicated project.
The Agile model's main benefits in software development are the ability to make changes, better control, higher customer satisfaction, continuous improvements, and fast delivery.

Evgeniy Altynpara is a CTO and member of the Forbes Councils’ community of tech professionals. He is an expert in software development and technological entrepreneurship and has 10+years of experience in digital transformation consulting in Healthcare, FinTech, Supply Chain and Logistics
Give us your impressions about this article
Give us your impressions about this article