How Smart Contracts in Blockchain Improve and Secure Business Processes
Updated 11 Jun 2023
18 Min
3328 Views
The terms “blockchain contracts'' or “smart contracts'' have been in the IT sphere picture for more than two decades. And as the digital info field was gradually spreading the good word about this technology, it reached the ears of other industries, too. Logistics and supply chain, insurance and healthcare discovered the ability of blockchain smart contracts to ensure prompt and secure agreements fulfillment.
While up until recently all the above was only a wonderfully appealing theory, today, in 2022, a blockchain smart contract is successfully integrated in multiple business and societal processes and the scale of its spread keeps growing. Below we have the blockchain smart contracts explained through and through, including the way they work, why trusting them is reasonable and how to benefit from their implementation. Dive in!
What Is a Smart Contract?
So, let’s get smart contracts explained. Basically, it is a program immersed in the blockchain and stored there as one of the chain’s blocks. The program, or the contract, can include many elements, but the essence of it stands for the basic “if/else” formula. Explaining how a smart contract works, we should highlight the role played by its conditions: unless the conditions are fulfilled the contract cannot be executed.
Also, talking about what is a smart contract in blockchain, the financial side should not be forgotten. In the case of the blockchain smart contracts, cryptocurrency is a unit of money used in financial transactions covered by the contract. That is why smart contracts are often referred to as crypto contracts.
Thus, the crypto smart contract’s fulfillment is triggered by completing the conditions written in it. In contrast to the paper contract, the content of the smart contract cannot be neglected or tampered with because of the unique properties of the latter. In particular, as smart contracts function on the base of the blockchain, each of them is created as its new block. This gives the crypto contract its main properties: immutability, distributiveness, absence of third parties, and automatic execution.
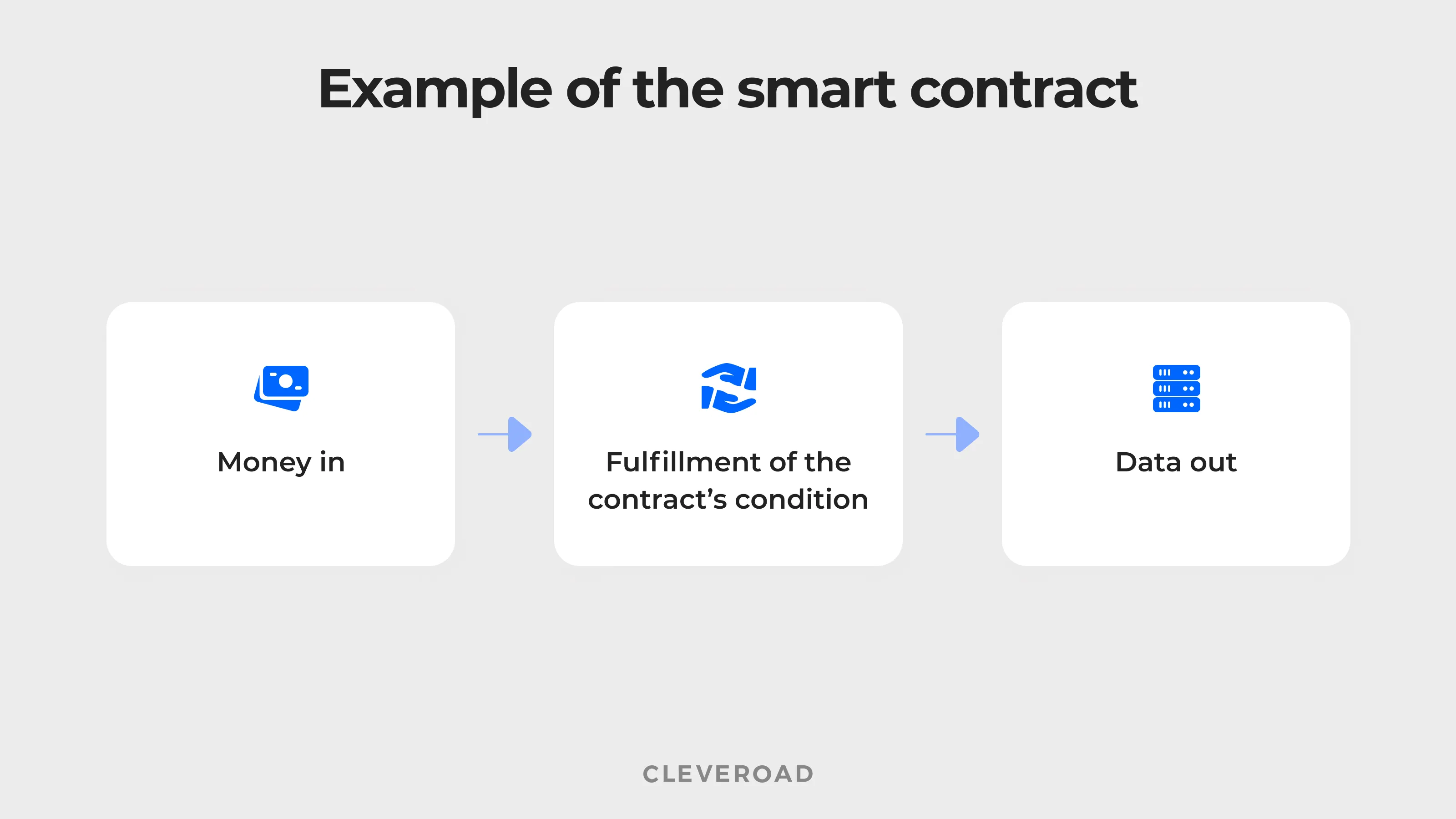
Example of smart contracts’ functioning.
Thus, smart contracts definition consists of several main elements. Each of these elements implies certain repercussions beneficial for the potential smart contracts’ user. So what does a smart contract do for the agreement through the perspective of the technology’s main features? Let’s take a quick look!
Immutability
- Contract's conditions cannot be altered in any way
- Various checks, including timestamping, are possible in real-time and non-stop modes
Distributiveness
- Tampering with conditions isn’t possible due to the contract’s settings
- Verification of transactions by all the chain’s participants
- No one is in charge more than anybody else
Absence of third parties
- Fast and efficient process of the contract’s conclusion and fulfillment
- No risk of biased approach in case of disputable situations between the parties
- Mitigation of the advance trust factor
How Do Smart Contracts Work?
As we already have smart contracts explained in terms of their definition and benefits they bring, it’s time to go deeper and uncrack the way they work.
First of all, smart contracts function inside the blockchain and align to its organization specifics.That is why before we discuss the working principles of smart contracts, blockchain definition should be revealed in short.
Blockchain is the system primarily created to make financial transactions fully secure and protect record keeping from being tampered. It can be imagined as a great digital hive where each separate cell has a stable location while its content (its honey) cannot be altered. Inserted data is literally a part of the chain (one piece of data is block), so changing one link would require changing all the preceding particles. This is an unmanageably tall order because even creating a new block (mining) is a real mathematical and programming challenge.
Blockchain is an example of the decentralized database, aka Decentralized Ledger Technology (DLT). DLT has its copies stored on every participant’s computer. So, when the code of smart contracts is entered in the ledger from one computer-participant (or node) it is automatically added to every computer participating in the blockchain.
Curious to know more about how blockchain works? Then the next video is worth checking:
Blockchain Solutions for Business: Advantages and Challenges
Just like with the transfer of crypto, with smart contracts the process also begins in the user wallet. But though the blockchain launches a smart contract identically to any of its transactions, there are features that define smart contract transactions as different from the regular ones.
- Such “smart” transactions already contain a compiled code of the smart contract (which is similar to a digital DNA that will later evolve into a full-scale digital body inside of the blockchain).
- In order to properly locate smart contracts, blockchain uses the second unique attribute of the smart contract’s transaction - receiver address.
Transactions complying with these requirements deliver smart contracts in blockchain, where new blocks for them are added by the traditional means of mining. Then the code unpacks itself and the contract is added to the blockchain in its full form.
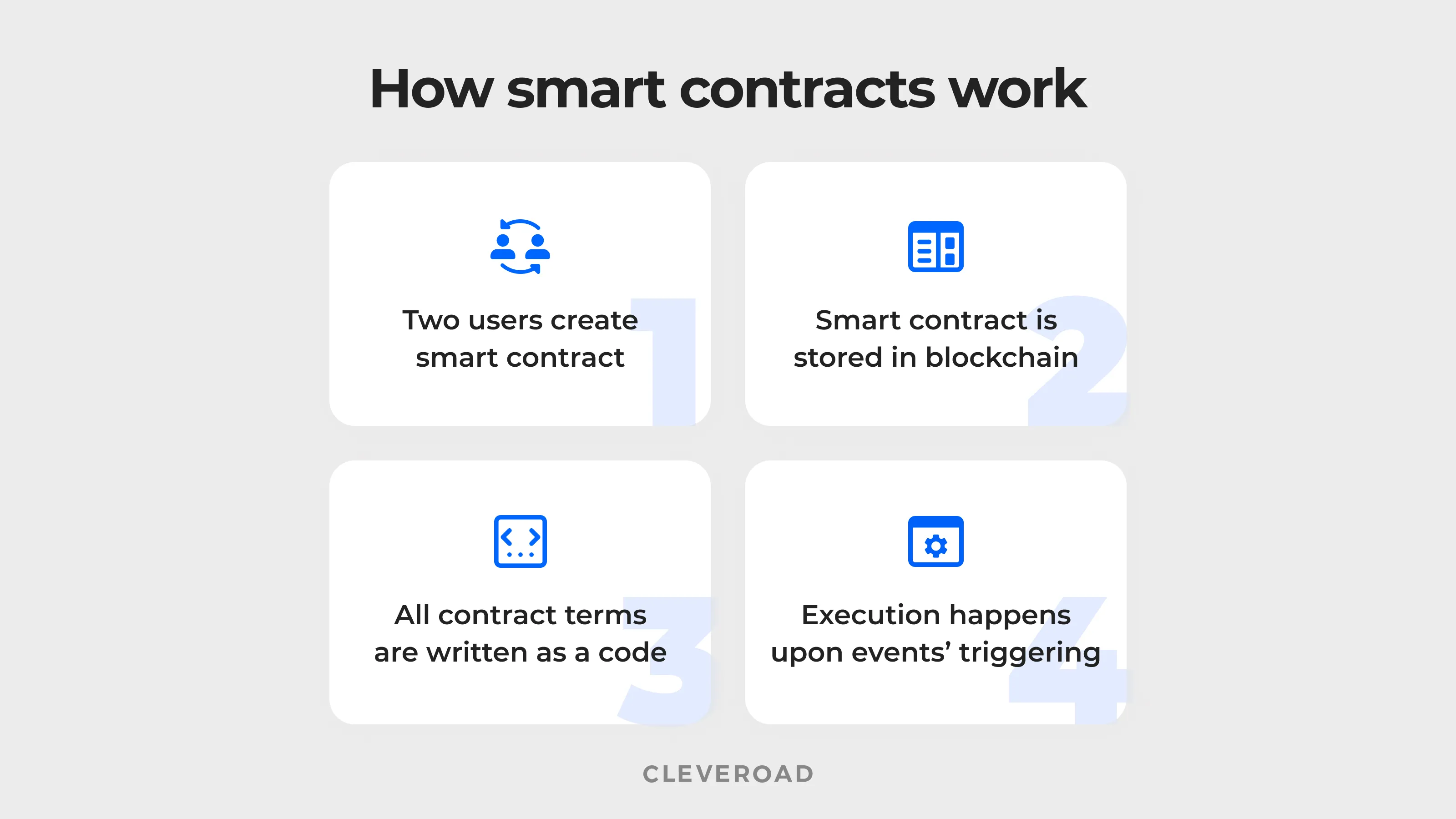
A blueprint of a smart contract’s functioning.
Find out more about cutting-edge tech alliances of blockchain, such as with Blockchain cloud computing!
Why does a blockchain need a smart contract?
As the technology of smart contracts becomes more and more popular, every blockchain framework out there faces that question. So what factors constitute to the smart contract meaning for the blockchain:
- Secure and effective way of running crypto deals for individual participants
- Efficient fund management for the group of people (i.e. multi-signature accounts)
- Facilitation of financial transactions between different contracts
- Permanent storage of data
- Optimization of crypto currencies transactions
And when it comes to interactions with crypto, what is a smart contract’s range of capabilities? As a matter of fact, it is pretty wide. Smart contracts crypto transactions allow end clients to send and receive payments, exchange assets, and run international business.
What You Need to Create a Smart Contract?
Now that we have the peculiarities of a smart contracts blockchain explained, let’s consider what are the compounds engaged in a smart contract’s creation. First of all, What are smart contracts’ key pillars? There are 3 basic compounds without which the existence of crypto contracts are simply unimaginable:
Blockchain
The first thing you need to do is create a smart contract. Currently, many blockchains have enabled their users to use cryptocurrency smart contracts in one way or another. A few examples of what are crypto smart contracts friendly blockchains would be Ethereum, Bitcoin, NEO, Hyperledger, Waves, etc.
Programming Language
All smart contracts are written in specifically tailored programming languages. Excellent illustrations of what blockchain smart contracts’ languages exist out there, are Ethereum blockchain Ethereum’s Solidity and Vyper.
Cryptocurrency
The next critical question is: do smart contracts require cryptocurrency to be deployed on the blockchain? In most cases the answer is ‘yes’. Most smart contract-friendly blockchains use their home cryptocurrencies to run relevant transactions.
What does a smart contract look like? It’s important to keep in mind the answer to that question for the clear image of the creation procedure. And since the smart contract looks like the program code, the stages of the smart contracts creation are similar to that of an application:
- Preparation of the software needed to write the contract’s code
- Identification of the contract’s goals and corresponding development of its architecture
- The contract’s deployment to the blockchain
Writing a smart contract is available for every user who knows how to code in the language, and has enough computer power to deploy the transaction, which every smart contract is from the technical side. Still, if you would like to skip this part and come straight to the result, you can always do that by using a hand of professionals. With a reliable software vendor by your side, you won’t have to figure out how it works on your own - they will do it for you.
Main ways to use smart contracts
There is an arrow of industries where smart contracts can be implemented, but the following 6 ones proved themselves the most beneficial.
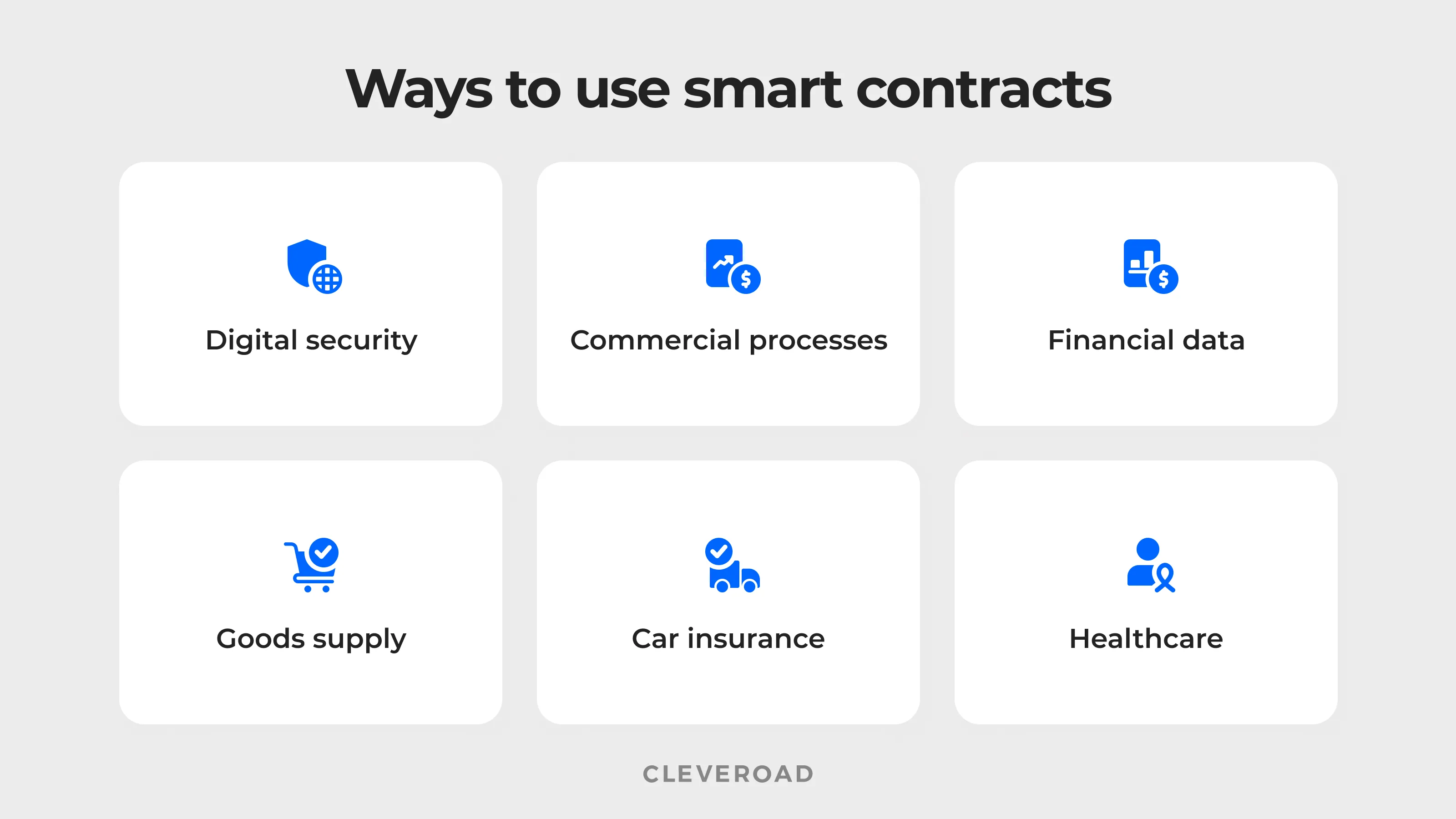
Top 6 ways to use smart contracts
Supply chain
Smart contracts enable coherent monitoring and control across the supply chain in real-time mode. Thanks to the blockchain technology, the transfer of goods can be tracked from the warehouse to the store shelves. Blockchain provides a unique environment where all parties of the supply chain have an equal decentralized access to the data about the goods. The data’ s security is guaranteed by the smart contracts’ mechanism allowing to conduct trustworthy business relationships among non trusted parties.
Alongside, as the execution of the smart contract is only possible if relevant conditions of its code are fulfilled, implementation of this technology into the supply chain domain results in a crucial boost of effectiveness and reliability accoross every step of goods’ transfer. Combined with a high level of security and transparency, smart contracts are a technology of unique value for the supply chain.
Healthcare
Smart contracts help improve and modify clinical trials since they automate all data about patients and hand over information between clinics. Furthermore, smart contracts can improve and simplify the transfer of personal disease data to keep anonymity. Thus, the confidentiality of the patient will be protected.
Digital security
Bitcoin smart contracts, as well as smart contracts based on other platforms, make it possible to control your data, digital assets and so on. You can determine what data you will reveal to contracts, and what will be secured. Also, smart contracts help users bypass intermediaries when transferring digital securities. Automated payment of dividends and management of obligations occurs during this process.
Commercial processes
Smart contracts simplify commercial processes after each deal. All terms are indicated in the contract as well as all standards and certifications supplied services should comply with. In case of non-quality good supply, the vendor won't receive money and he/she will have to pay the penalty for the supply of non-quality service. Additionally, usage of smart contracts when you make international payments is very convenient. Contracts make faster payment for a bargain with a guarantee, that is known as a letter of credit as well. Also, the liquidity of financial assets is increased.
Financial data
Financial organizations can record financial data with the help of smart contracts. It will help combine all data in one register and simplify the exchange of information between organizations. It will lower expenses for audit and improve the financial reporting process. Additionally, smart contracts make it possible to automate mortgage payments processing and execute proper financial transfer without fraud.
Car insurance
As for car insurance, a smart contract can store insurance policy and the record with the history of driving. It is possible to send requests after an accident to the Internet of Things that will be installed in many cars in future, and it will make it possible to establish the cause of car accidents.
Why to Implement Smart Contracts Into Business Processes?
We have discussed some specific cases of smart contracts implementation in several industries where it has the most groundbreaking impact. In this part, let’s fly up to the height of universal profits that smart contracts can bring to your business regardless of the domain it belongs to.
Security
The list of benefits that a smart contract can bring to your business opens up with security. In a smart contract’s case, security is ensured by the blockchain inner working principles and configuration of the technology itself. Thanks to the proof-of-work procedure and distributed ledger’s settings, every smart contract is a piece of thoroughly verified data immune to hacker attacks.
Additionally, smart contracts guarantee transparency upon its fulfillment, thus providing a solid base for trustworthy business relationships between distrusted parties. After all, if all parties explicitly made their peace with the contract’s conditions from the get-go, the code will secure such agreement leaving no chance to cheat.
Speed and low cost
Enriching your business with smart contracts is also beneficial from the perspective of time and money spent. In contrast to regular standard contracts, crypto agreements do not require any third parties so you won’t have to spend precious time searching for a reliable intermediary. Besides, as the smart contract is basically a program code, no bureaucracy is involved in the process of its creation. Finally, automatic execution of such smart agreement enables a drastic reduction of engaged personale and, consequently, blockchain cost, as monitoring and trackage are conducted by the contract itself in a non-stop regime.
Standardization
All standard agreements we are used to, including digital ones, are drawn up by people. The language of law, or legalese, implies so much conformity and uniform style ruling in traditional legal documents, that standardization seems to be the law of nature in this realm. Indeed, it may be so, but only in terms of linguistics.
When it comes to standardization of the agreement itself so that it would suit any type of a contract, smart contracts are in the box seat. Being essentially a program written in a code following laws common for all such agreements, smart contracts come up as the most standardized form of an agreement.
Accuracy
Since the smart contract is a program that is automatically executed provided its predetermined conditions are actualized, you do not have to worry that the agreement will go wrong. Still need a sharper understanding of what is a smart contract and how does it work? An example will come in handy.
Let’s say a smart contract was created to regulate the delivery of grain with certain properties: impurity content, humidity condition, etc. The IoT devices installed at a grain elevator scan the environment and pass the real-time data to the blockchain, which subsequently transfers it to the smart contract. If relevant conditions predefined in the contract are met accurately, the contract is automatically executed (which in our example would correspond to confirmation of the purchase and a relevant crypto transfer).
Transparency
Reflecting on what is a smart contract blockchain’s greatest contribution to overall efficiency of real-world processes, transparency comes to mind as the first candidate. At the end of the day, fully reliable business relationships are impossible if someone is more in charge than others. Besides, complex large-scale interactions with a lot of middle steps to make before reaching a desirable outcome welcome as many pairs of eyes to witness their proper fulfillment as it is simply available.
Thanks to being located on a decentralized peer-to-peer network, a smart contract can be reached by all the network’s participants (as any of the blockchain’s transactions). Thus, every participant of a smart agreement can monitor its execution and verify whether the conditions are fulfilled and if not, identify the responsible. At the same time, all participants can maintain full confidentiality as smart contracts do not require revealing real-world identities to keep the agreement valid.
Want to build a DEX? Check our tech guide on its proper implementation
Autonomy
One of the best things about how a smart contract works is its capacity to function independently from any additional regulator. As soon as smart contracts are integrated into the blockchain, it becomes an independent digital unit that realizes its goal in a deterministic and predictable manner.
Thus, you can be sure that idea you’ve decided to embody by the means of a smart contract immune to any malicious interruptions or unauthorized changes. In this regard, a smart contract is like a time capsule dug in the decentralized lands of the blockchain ruled by everyone who uses it and yet anyone in particular.

Reasons to implement smart contracts.
What to Consider When You Implement Smart Contracts?
As with any other advanced technology that is at the dawn of its existence, smart contracts’ implementation is connected to certain challenges. Let’s look at the dark sides of smart contracts: what are they and how to get around them effectively?
Low flexibility
Once the smart contract is written, it is impossible to make changes or updates in it.
Solution: All terms of smart contracts should be checked and double checked at the very beginning of the implementation process. In addition, one smart contract can be canceled with the help of another smart contract.
Human factor
Despite being a fully digitized form of the agreement, smart contracts are still written by people. And as long as the contract is immutable, one mistake can result in a cascade of financial losses.
Solution: To stay on the safe side, smart contracts’ creation is better to entrust to the reliable team of developers with profound expertise in fin tech software.
Blockchain tech settings
Smart contracts rely on the relevant information entry to incentivize their execution. However, blockchain, and hence smart contracts as its inherent part, do not have a direct access to real-time data about the outside world.
Solution: This challenge is successfully overcome by Oracles, the data feeding platforms that retrieve data from the external world and then send it to a smart contract through the blockchain mechanisms.
Uncertain legal status
Currently smart contracts do not have a set place in the legislation frame. This is connected with the distributive character of the technology blockchain’s general novelty and comparatively small representation outside the IT sector.
Solution: This problem is already being gradually solved as the government authorities begin to care about the web field of their countries no less than the physical one.
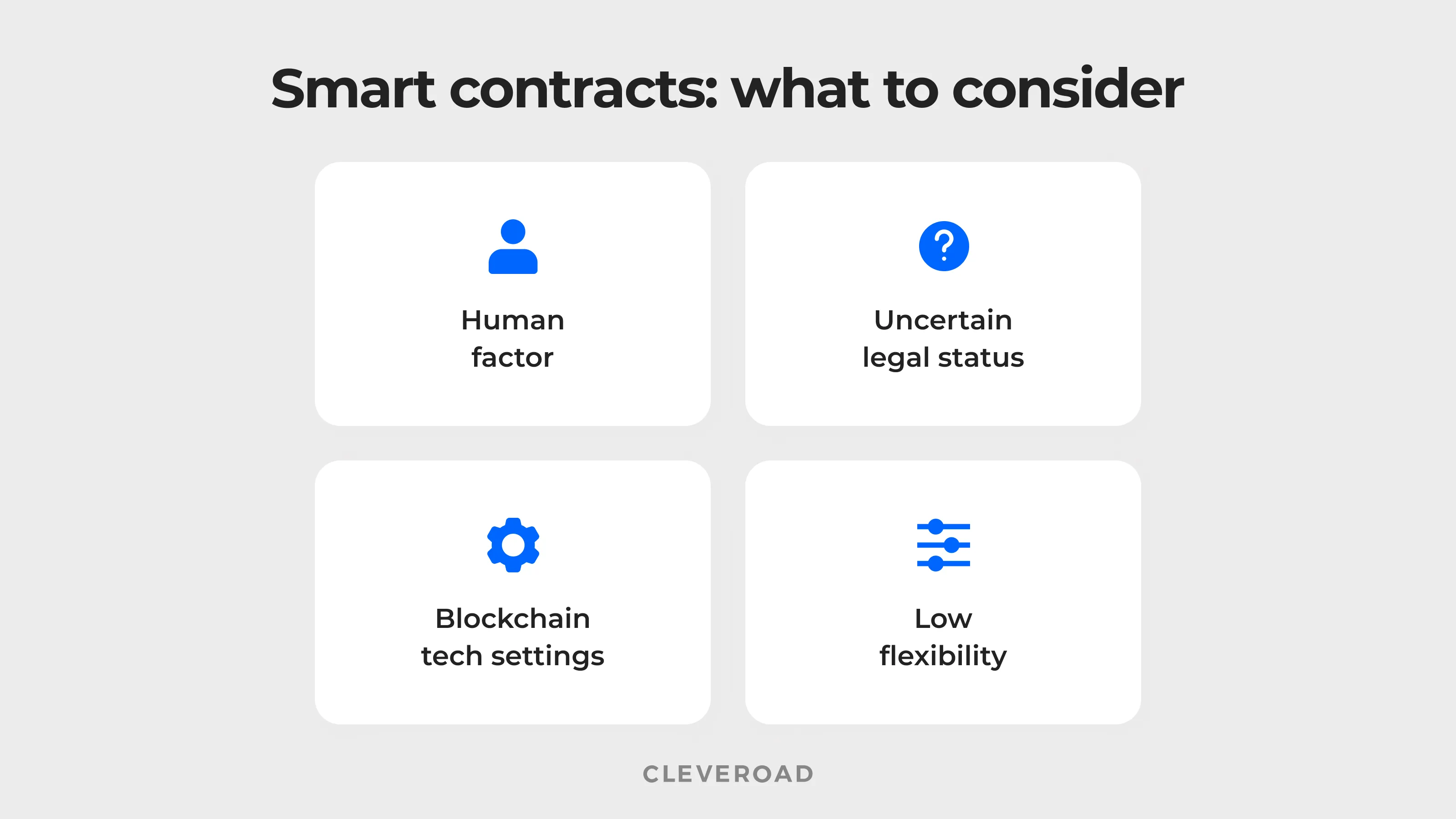
What to consider when implementing smart contracts.
The Future of the Blockchain Smart Contracts in Business Solutions
Smart contracts already facilitate many needs of the modern day business domain and real-world cases. But what is the meaning of smart contract technology for the future?
The future of a technology reveals itself through its compatibility with other cutting-edge achievements marked with rapid development. Smart contracts have proved themself both beneficiary and a supplementation essential for the progress of a whole arrow of tech breakthroughs. Let’s look more precisely at some of them.
The Internet of Things
As we have already mentioned, smart contracts cannot draw information about the outside world without the assistance of intermediaries. Oracles is a technology that performs the role of the bridge between the smart contracts and the external data sources today. This technology is not perfect, however, as the information is supplied from the data feeds and directly from reported conditions or objects. The Internet of Things makes it different. IoT devices retrieve real-time data straight from the surrounding environment via their embedded systems, mainly represented by various sensors.
As IoT devices are growing in numbers (their amount is predicted to reach 30.9 billion of connected units by 2025), the inflow of information provided by them is to outreach both scale and quality of any data feed. That factor of informational quality plays a decisive role for the smart contracts’ proper utilization: this is how the contract gets to know whether its conditions are fulfilled and subsequently decides whether it’s time to execute itself.
In exchange for such huge benefits, smart contracts too can make a groundbreaking contribution for the Internet of Things’s evolution. Particularly, as smart contracts grant automatic execution of certain outcomes based on predetermined conditions, IoT devices could use them to automatically incentivize relevant responses to the environment's actualities.
Know more about the Internet of Things and the opportunities it brings to the supply chain: Blockchain and IoT in Supply Chain and Logistics: The Impact of Digitalization Trends!
Edge computing
Again, talking about what is a crypto smart contract’s next development perspective, its dependency on the efficient data processing is worth keeping in mind. Huge information flux outpouring the blockchain is both a privilege and a burden of the system, including the smart contracts’ share. On the one hand, smart contracts rely on the sufficiency of supplied data in its execution. On the other hand, storing a processing of such big data as the blockchain needs to sustain smart contracts agile operation requires immense energy, time, and finance spend.
And this is the point where edge computing comes to the rescue. Edge computing is a principle of data storage based on a distributed network of connected data sources, mainly consisting of edge servers and IoT devices. All information transactions take place within the direct reach of engaged applications. So basically edge computing technology minimizes the time spent and maximizes efficiency of the bandwidth use. As a result, edge computing can help blockchain optimize its data storage and processing and thus bring smart contracts productivity to the new level.
Decentralized applications
Thinking about what is a smart contract blockchain implementation available for users with a profile tech expertise, decentralized applications (dapps) pop up in mind front and center. What differs a dapp from an app is the location of the former on the blockchain network, in particular, Ethereum. The dapp has got a user-friendly frontend of a traditional app (users can pick any language to write the code), while a smart contract functions as its backend.
Among the dapps’ advantages over centralized applications, fail-safety of its operations is the most important one. This is achieved via the innate properties of a peer-to-peer network.
First, deterministic configuration of dapps ensures their permanent functioning independently of any human administrator and regardless of the environment conditions. Second, decentralized storage makes dapps immune to hacker attacks trying to mess with their operation. Finally, a decentralized app enables its users to keep the incognito and utilize it under a false identity.
How Cleveroad Can Help You With Smart Contracts
Today more and more people use different blockchain platforms to complete smart contracts. One of the major drawbacks of such platforms is their functional unfriendliness to the users who do not have profile expertise in the field. The above is especially true when it comes to smart contracts. Additionally, blockchain platforms tend to limit user’s abilities to customize their smart contracts, offering only a minimal amount of the contracts’ patterns.
If you are planning on integrating a customized smart contract into your business, but do not want to immerse yourself deep into technical peculiarities of the process, a team of experienced developers is the best choice. Developers will also use blockchain platforms, but thanks to the significantly higher command of technical skills, they will be able to leverage the blockchain mechanisms in a much more prompt and efficient manner.
Cleveroad is a software company based in Northern Europe, Estonia that brings smart solutions accompanied with a cogent expertise right to our clients’ fingertips. For more than a decade we have provided our customers with professional assistance, having gained an especially solid expertise within the domain of financial technologies.
We offer:
- Practical and confirmed fin tech expertise
- Best technological solutions: clouds, advanced business architecture, well-judged intermediaries
- Profound experience in the integration of IT decisions into active business processes, systems scaling, end-to-end support
- Flexible collaboration models with the accent on your budget optimization
Get the most of smart solutions
Leverage the smart contracts and embody your idea with the team of fintech experts!
A smart contract is a computer algorithm that is developed for the conclusion and endorsement of self-executing contracts that are implemented in a blockchain environment. Such contracts are written in the code form that exists in the distributed register called blockchain, and this register is maintained and managed by the network of computers. Smart contracts make it possible to exchange money, assets, property etc., safely and directly without any intermediaries.
Here’s the list of the most common use cases for smart contracts:
- Supply chain
- Healthcare
- Digital identity
- Commercial processes
- Financial data
- Car insurance
Smart contracts are based on blockchain technology. In short, it is a distributed register that looks like a decentralized system and it is located on many computers that are connected to one network. Blockchain makes it possible for users to make transactions, transfer information and securities without banks and intermediaries.
And what is the principle of smart contracts functioning? First assets and contract terms are coded and put into blockchain block, then a contract is stored distributedly on a large number of nodes and it is fulfilled when terms are activated. Fulfillment of obligations by parties is verified automatically.
Here are the benefits of using smart contracts over traditional ones:
- Security
- Speed and low cost
- Standardization
- Accuracy
- Transparency
- Autonomy
Here are the downsides of using smart contracts:
- Low flexibility
- Human factor
- Blockchain tech settings
- Uncertain legal status
Smart contracts make all operations secure by encrypting and storing all contracts distributively. Besides, all involved parties can monitor the progress of the deal in real time which makes all operations completely transparent.

Evgeniy Altynpara is a CTO and member of the Forbes Councils’ community of tech professionals. He is an expert in software development and technological entrepreneurship and has 10+years of experience in digital transformation consulting in Healthcare, FinTech, Supply Chain and Logistics
Give us your impressions about this article
Give us your impressions about this article